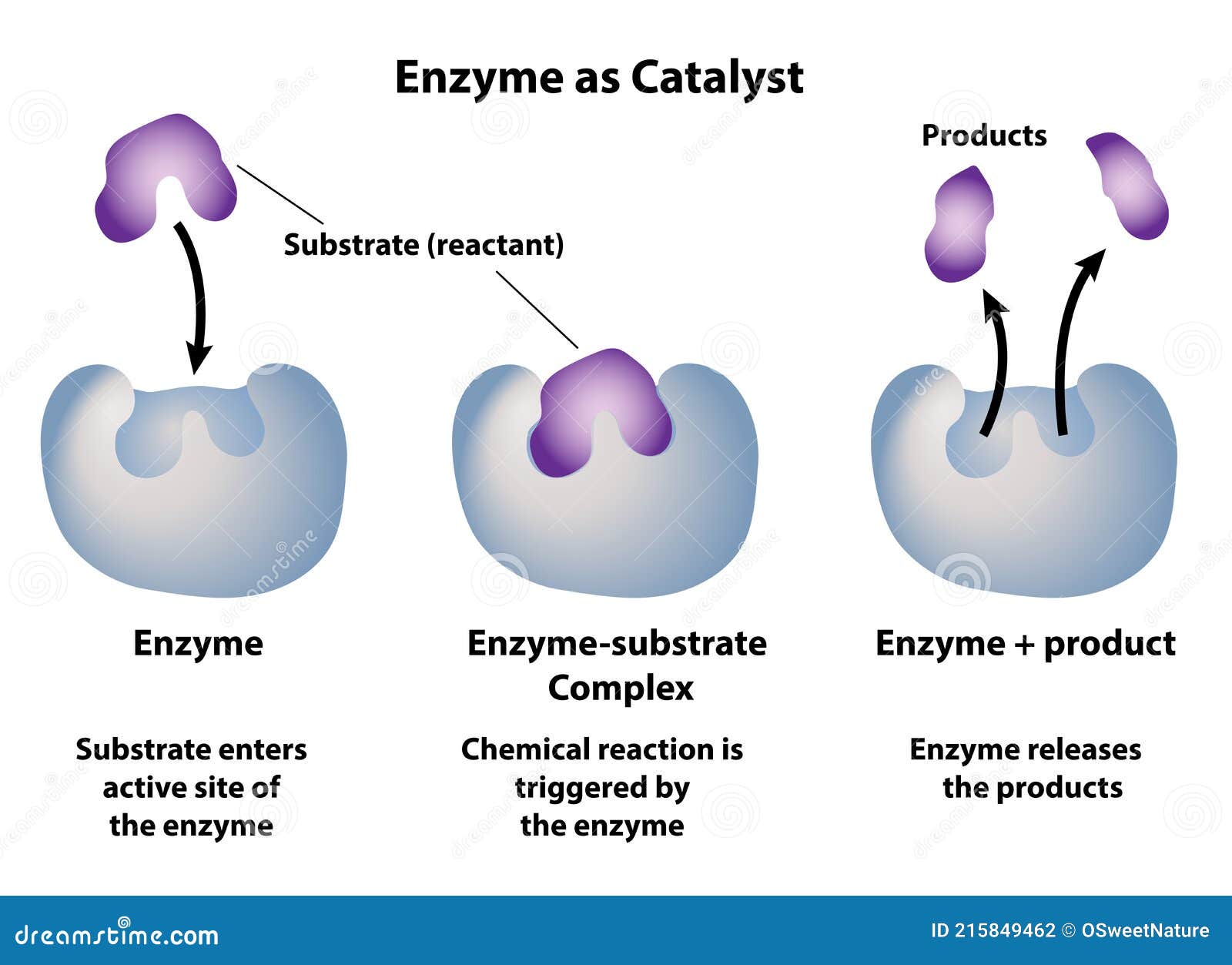
Enzyme Substrate Equation . E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity is only limited. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that.
from animalia-life.club
The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity is only limited. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the.
Enzyme Substrate Complex Equation
Enzyme Substrate Equation E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity is only limited. E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Enzyme Substrate Equation Enzyme Substrate Equation The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that. E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. The equation was an attempt to. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From animalia-life.club
Enzyme Substrate Complex Equation Enzyme Substrate Equation The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. The general approach is to. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 2 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2434627 Enzyme Substrate Equation E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From animalia-life.club
Enzyme Substrate Complex Equation Enzyme Substrate Equation For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity is only limited. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. The equation was an attempt to explain. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From animalia-life.club
Enzyme Substrate Complex Equation Enzyme Substrate Equation The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From ibiologia.com
Substrate Definition , Biochemsitry & Examples Enzyme Substrate Equation E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity is only limited. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \]. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzyme … the Biological Catalyst PowerPoint Presentation, free Enzyme Substrate Equation Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that. The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins.. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.sliderbase.com
Enzymes. A Cell's Catalysts Presentation Biology Enzyme Substrate Equation The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. E + s ↔ es. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 6. Metabolism & Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation ID562848 Enzyme Substrate Equation The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 6.3 Enzyme PowerPoint Presentation, free Enzyme Substrate Equation \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that. E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. Enzyme reactions do not show simple. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chemical Reactions and Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free Enzyme Substrate Equation \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. E + s ↔ es. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From animalia-life.club
Enzyme Substrate Complex Equation Enzyme Substrate Equation \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Enzyme Substrate Equation Enzyme Substrate Equation E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity is only limited. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.genome.gov
Enzyme Enzyme Substrate Equation \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.researchgate.net
EnzymeSubstrate Binding as an Analog Circuit Schematic The Enzyme Substrate Equation The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity is only limited. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.dreamstime.com
Substrate and Enzyme in Catalytic Cycle Stock Vector Illustration of Enzyme Substrate Equation For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product and hence the reaction velocity is only limited. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ] {k_2} e + p \] the enzyme interacts. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From www.vrogue.co
Biochemistry Enzyme Basic Concept vrogue.co Enzyme Substrate Equation E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. The equation was an attempt to explain the behaviour of an enzyme (binding of substrate and subsequent catalysis) long before the exact nature of enzymes as proteins. Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. \[ e + s \xrightarrow[ ]{k_1}[ es ] \xrightarrow[ ]. Enzyme Substrate Equation.
From babbish77549.blogspot.com
Enzyme Activity Calculation Formula Enzyme Substrate Equation Enzyme reactions do not show simple zero, first or second. The general approach is to add a known concentration of substrate to the enzyme and to determine the initial reaction rate for that. E + s ↔ es ↔ e + p, where e is the. For a kinetically perfect enzyme, every encounter between enzyme and substrate leads to product. Enzyme Substrate Equation.